XML Syntax - SELECT Clause
This extended version of the SELECT clause assigns a filename to an XML stream.
Format
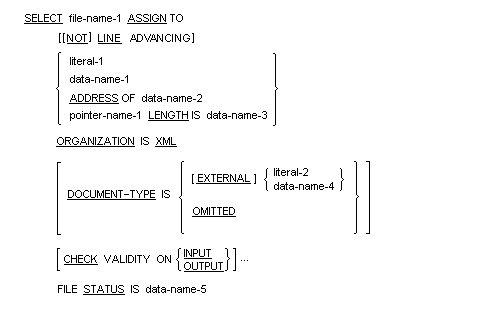
Syntax Rules:
- File-name-1 is the name of the file that contains the XML stream.
- LINE ADVANCING specifies that line feeds are included in the output.
- NOT LINE ADVANCING specifies that no line feeds are included in the output.
- Literal-1 must be an alphanumeric literal.
- Literal-1 or data-name-1 must be a COBOL file specifier.
- Data-name-2 is an alphanumeric data item that contains XML data at run time.
- Pointer-name-1 is the address a memory buffer containing XML data.
- Data-name-3 is the length of the buffer pointed to by pointer-name-1.
- EXTERNAL indicates that the schema this XML stream conforms to is external. This is for documentation purposes alone and does not affect input or output.
- OMITTED specifies that no schema is associated with the XML file.
- Literal-2 or data-name-4 is a generated or external name of the schema the record conforms to. For example, for an external schema, this could be an entire URL to the file such as "http://www.microfocus.com/nx40/cobol/v2.0/foo.xsd"
- Data-name-5 must be declared in the data division as a PIC S9(9) (any usage) and holds the file status for the last I/O operation.
General Rules:
- When neither LINE ADVANCING nor NOT LINE ADVANCING is specified, line feeds are included in the output.
- Literal-1 or data-name-1 in an application that is not Web-based can be a COBOL file specifier as follows:
- stdin, use ":CI:"
- stout, use ":CO:"
- file, use
".myxmlfile"
where myxmlfile is the name of the file. Generally, XML files use the file extension .xml.
- pipe, use
"<myprog, ">myprog" or "|myprog"
where myprog is the name of a program that uses stdin and/or stdout to communicate through the pipe.
- Literal-1 or data-name-1, in a client-side Web-based application, can be:
- A CGI program hosted on a Web site, such as "http://www.bookdb.com:80/cgibin/xmlprog.exe"
- An XML file, such as or "http://localhost/xmlfile.xml"
- Literal-1 or data-name-1, in a CGI, server-side Web application can be ":CGI:", which causes the environment variable CONTENT_LENGTH to be considered when reading the standard input stream (stdin). ":CGI:" can only be opened INPUT or OUTPUT, never I-O or EXTEND.
- When DOCUMENT-TYPE is not specified, no schema is associated with the XML file. For example:
The following code:
SELECT xml-addressdb ASSIGN 'address.xml' ORGANIZATION IS XML DOCUMENT-TYPE IS OMITTED FILE STATUS xml-status.Is equivalent to:
SELECT xml-addressdb ASSIGN 'address.xml' ORGANIZATION IS XML FILE STATUS xml-status. - The CHECK clause can be repeated multiple times. For example:
SELECT foobar ASSIGN TO "foobar.xml" ORGANIZATION IS XML DOCUMENT TYPE IS "foobar.xsd" CHECK VALIDITY ON INPUT CHECK OUTPUT.